Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology is a fundamental textbook designed for students, offering a comprehensive overview of human anatomy and physiology․
It provides clear explanations of complex biological processes, making it accessible for learners with limited prior science knowledge, and supports clinical applications․
1․1 Overview of Human Anatomy and Physiology
Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology provides a foundational understanding of the human body’s structure and function․ It covers the organization of the body, from cells to systems, explaining how organs and tissues interact to maintain life․ The textbook emphasizes clinical relevance, connecting anatomical structures to physiological processes․ Designed for students, it ensures a clear and accessible learning experience, aligning with course requirements for introductory anatomy and physiology studies․
1․2 Importance of Studying Anatomy and Physiology
Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology highlights the importance of studying these fields for understanding the human body’s structure and function․ Anatomy and physiology are crucial for careers in healthcare, enabling professionals to diagnose and treat conditions effectively․ They also promote a deeper appreciation of human health, disease prevention, and overall well-being․ The textbook underscores how these disciplines form the cornerstone of medical knowledge, essential for both practitioners and informed individuals․
1․3 Key Concepts and Terminology
Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology introduces foundational concepts such as cells, tissues, organs, and systems․ Key terminology includes anatomy (structure) and physiology (function), emphasizing how they interrelate․ Understanding terms like homeostasis, feedback mechanisms, and body systems is crucial for grasping human biology․ These concepts provide a framework for exploring complex processes, ensuring a solid foundation for further study in health and life sciences․
Skeletal and Muscular Systems
The skeletal system provides structure and support, while the muscular system enables movement․ Together, they facilitate motion and maintain posture, as explained in the textbook․
2․1 Structure and Function of Bones
Bones are rigid, calcified structures forming the skeleton․ They provide support, protection, and facilitate movement․ The structure includes compact and cancellous bone tissue, with a periosteum covering․ Their function involves blood cell production, mineral storage, and serving as attachment points for muscles․ The textbook explains how bones classify into long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid types, each adapted for specific roles in the skeletal system․
2․2 Joints and Their Classification
Joints, or articulations, are points where bones meet, enabling movement, stability, and shock absorption․ They are classified into three structural types: fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints․ Fibrous joints are immovable, while cartilaginous allow limited movement․ Synovial joints, the most common, facilitate wide-ranging motion and include hinge, ball-and-socket, and pivot types․ Joints play a crucial role in locomotion and maintaining posture, supported by ligaments, tendons, and synovial fluid to reduce friction and enhance functionality․
2․3 Muscle Types and Their Roles
Muscles are categorized into skeletal, smooth, and cardiac types․ Skeletal muscles, attached to bones, enable voluntary movements and maintain posture․ Smooth muscles, found in organs, facilitate involuntary actions like digestion․ Cardiac muscle powers the heart’s contractions, ensuring blood circulation․ Each type has distinct structures and functions, working synergistically to support movement, organ function, and overall bodily processes․ Understanding their roles is essential for grasping human physiology and the mechanisms behind locomotion and internal operations․
Nervous and Circulatory Systems
The nervous system regulates body functions through nerve impulses, while the circulatory system transports oxygen and nutrients via blood․ Together, they maintain homeostasis and enable responses to stimuli․
3․1 Components of the Nervous System
The nervous system comprises the central nervous system (CNS), including the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), consisting of nerves and ganglia․
The CNS processes information and controls voluntary and involuntary functions, while the PNS connects the CNS to sensory receptors and effectors, enabling communication and response․
3․2 Blood Circulation and Heart Function
The circulatory system, led by the heart, is vital for transporting oxygen, nutrients, and hormones throughout the body․ The heart, a muscular organ, pumps blood through arteries, veins, and capillaries․ Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart, while veins return oxygen-depleted blood․ Capillaries facilitate the exchange of substances between blood and tissues․ This system maintains cellular function and overall health, as outlined in Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology․
3․3 Relationship Between Nervous and Circulatory Systems
The nervous and circulatory systems are deeply interconnected, with the nervous system controlling cardiovascular functions․ The autonomic nervous system regulates heart rate and blood vessel diameter, ensuring proper blood flow․ This interaction is crucial for maintaining homeostasis, as described in Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology․ The nervous system’s control over circulation ensures oxygen and nutrients are efficiently delivered to tissues, supporting overall physiological function and health․

Digestive and Respiratory Systems
The digestive system breaks down food for nutrient absorption, while the respiratory system facilitates gas exchange․ Both systems are vital for energy production, as explained in Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology․
4․1 Process of Digestion and Absorption
Digestion begins in the mouth, where food is chewed and mixed with enzymes․ The esophagus transports food to the stomach, where gastric juices break it down further․ In the small intestine, enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver process nutrients, allowing absorption into the bloodstream․ The large intestine absorbs water and eliminates waste․ Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology details this process, emphasizing the role of enzymes and absorption mechanisms․
4․2 Mechanisms of Breathing and Gas Exchange
Breathing involves the coordinated effort of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, enabling inhalation and exhalation․ Inhalation expands the chest cavity, lowering pressure, while exhalation is passive․ Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli, where oxygen diffuses into the blood and carbon dioxide is removed․ This process is vital for cellular respiration․ Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology explains these mechanisms in detail, emphasizing their importance in maintaining homeostasis and overall physiological function․
4․3 Importance of Nutrition for Physiological Functions
Nutrition is essential for maintaining physiological functions, as it provides the body with the necessary nutrients, vitamins, and minerals․ These elements support energy production, tissue repair, and immune function․ Proper nutrition ensures optimal functioning of all body systems, including the digestive, circulatory, and nervous systems․ A balanced diet helps prevent deficiencies and chronic diseases, promoting overall health and well-being․ Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology highlights the critical role of nutrition in sustaining life and supporting physiological processes․

Endocrine and Integumentary Systems
The endocrine system regulates hormones, while the integumentary system protects the body․ Both systems are vital for maintaining homeostasis, growth, and overall physiological balance․ Holes Essentials provides detailed insights․
5․1 Hormones and Their Regulatory Roles
Holes Essentials explains hormones as chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands, regulating various bodily functions․ They control metabolism, growth, and reproductive processes, ensuring internal balance and proper organ function․ The textbook highlights how hormones like insulin and thyroid hormones maintain homeostasis, illustrating their essential roles in health and disease․ This section provides a clear understanding of hormonal regulation, crucial for students studying anatomy and physiology;
5․2 Structure and Functions of the Skin
The skin is the body’s largest organ, consisting of the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis․ It protects against external damage, regulates temperature, and facilitates sensory perception․ The epidermis, with keratinocytes, provides a protective barrier, while the dermis contains connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerve endings․ The hypodermis, rich in fat, offers insulation and cushioning․ Beyond protection and thermoregulation, the skin produces vitamin D, aids in excretion, and supports immune functions with Langerhans cells; These roles are essential for maintaining overall health, as explained in the ‘Holes Essentials’ textbook․
5․3 Interaction Between Endocrine and Integumentary Systems
The endocrine and integumentary systems interact through hormones influencing skin functions․ For instance, hormones regulate skin pigmentation and metabolism․ The skin produces vitamin D upon sun exposure, acting as a hormone․ Additionally, endocrine hormones like adrenaline cause skin responses such as sweating․ This interplay is vital for maintaining homeostasis and overall bodily functions, as detailed in the ‘Holes Essentials’ textbook․

Urinary and Reproductive Systems
The urinary system filters waste and regulates fluids, while the reproductive system manages the production and development of offspring, both essential for maintaining life and health․
6․1 Kidney Function and Urine Formation
The kidneys play a vital role in filtering blood, removing waste products, and regulating fluid balance in the body․ They process approximately 200 liters of blood daily, producing urine that contains excess water, salts, and waste metabolites like urea․
Urine formation begins with filtration in the nephrons, the functional units of the kidneys․ Blood is filtered through capillaries in the glomerulus, and the filtrate is modified as it passes through the renal tubules, where essential nutrients and water are reabsorbed․ This process ensures the maintenance of proper electrolyte balance, pH levels, and hydration, crucial for overall physiological function․
6․2 Reproductive Organs and Their Functions
The male reproductive system includes the testes, which produce sperm and hormones like testosterone, and the penis, which delivers semen during ejaculation․ The female reproductive system features the ovaries, which produce eggs and estrogen, the uterus, which supports fetal development, and the vagina, serving as the birth canal and passageway for menstrual flow․ These organs work together to enable reproduction, maintaining the species through fertilization and pregnancy; Proper function ensures sexual health and genetic continuity․
6․3 Connection Between Urinary and Reproductive Health
The urinary and reproductive systems share anatomical structures, such as the pelvic region, and are closely linked in function․ Infections or disorders in one system often affect the other, as seen in conditions like urinary tract infections (UTIs) impacting reproductive health․ Maintaining proper urinary function supports reproductive processes, and vice versa, highlighting the interconnectedness of these systems for overall physiological balance and sexual well-being․

Special Senses
Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology explores the mechanisms of vision, hearing, and other senses, emphasizing their critical roles in interpreting and interacting with the environment․
7․1 Vision and the Eye
Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology details the structure and function of the eye, focusing on light refraction, lens accommodation, and the retina’s role in vision․ The text explains how the eye processes light to create visual perceptions, emphasizing the importance of the cornea, iris, and optic nerve․ It also discusses common vision disorders, such as myopia and hyperopia, and their physiological basis․ The book provides a clear understanding of how the nervous system interprets visual signals, ensuring comprehensive insight into human vision mechanisms․
7․2 Hearing and the Ear
Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology elaborates on the ear’s structure and its role in hearing and balance․ The outer ear collects sound waves, which travel through the middle ear and are amplified by the ossicles․ The inner ear’s cochlea converts vibrations into nerve impulses, enabling sound perception․ The vestibular system, including the semicircular canals, maintains balance․ The eustachian tube equalizes ear pressure, crucial for sound transmission․ This section provides a detailed understanding of auditory mechanisms and their physiological significance․
7․3 Other Senses and Their Mechanisms
Beyond vision and hearing, other senses like touch, taste, and smell play crucial roles in human physiology․ The sense of touch involves mechanoreceptors in the skin, detecting pressure, texture, and vibration․ Taste and smell rely on chemoreceptors, with taste buds identifying chemicals in food and olfactory receptors detecting airborne molecules․ Balance, regulated by the vestibular system, and proprioception, sensing body position, are also essential․ These senses integrate to provide a comprehensive perception of the environment, as detailed in Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology․
Overview of the “Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology” Textbook
Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology is a widely used textbook authored by experts like David Shier, Jackie Butler, and Ricki Lewis, offering clear, science-backed explanations suitable for students with limited prior knowledge․
8․1 Authorship and Editions
Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology is authored by David Shier, Jackie Butler, and Ricki Lewis․ It is available in multiple editions, including the 10th and 15th editions․ The 10th edition focuses on simplifying complex concepts for students without prior science knowledge․ The 15th edition includes updated content and clinical applications․ Both editions are widely recognized for their clarity and effectiveness in teaching anatomy and physiology․
8․2 Key Features of the Textbook
Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology is designed for one-semester courses, offering a clear, concise approach to complex topics․ It includes detailed illustrations, clinical applications, and review questions to enhance understanding․ The textbook assumes no prior science knowledge, making it ideal for beginners․ Supplementary materials like review packets and online resources support student learning․ Its structured format and focus on essential concepts make it a valuable resource for anatomy and physiology education․
8․3 Target Audience and Learning Outcomes
Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology is primarily designed for students in healthcare, biology, and related fields․ It caters to those with minimal science background, providing foundational knowledge of human anatomy and physiology․ The textbook aims to develop critical thinking skills and apply concepts to real-world scenarios․ Students can expect to gain a clear understanding of anatomical structures, physiological processes, and their clinical relevance․ Supplementary resources, such as review packets, further support academic success․

Study Resources and Aids
Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology offers review packets for chapters, such as muscle systems, and online resources like HiredSupport for additional learning support․
9․1 Supplements for Effective Learning
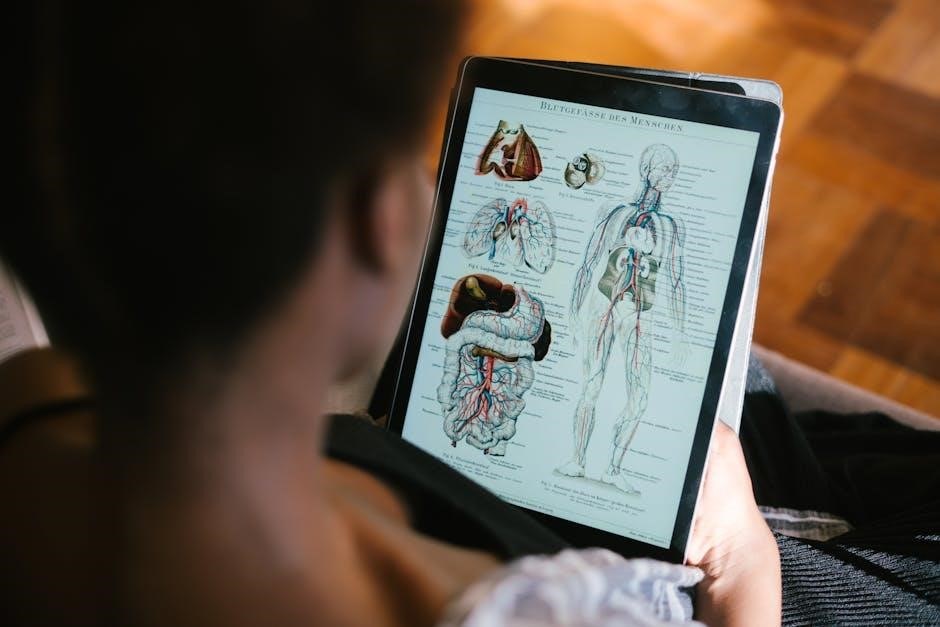
Supplements for effective learning include review packets for specific chapters, such as muscle systems, and online resources like HiredSupport for affordable IT and study tools․
These resources provide structured guidance, enhancing understanding of complex topics in Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, ensuring students can master the material efficiently and effectively․
9․2 Online Resources and Tools
Online resources and tools, such as downloadable PDF versions of Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, provide students with accessible study materials․
These resources include the 10th and 15th editions, available on platforms like cheaptodownload․com, offering immediate access to the full textbook for comprehensive learning․
Additional online tools, such as review packets for specific chapters, enhance understanding and retention of key anatomical and physiological concepts․
9․3 Tips for Mastering Anatomy and Physiology
Mastering anatomy and physiology requires active learning techniques, such as labeling diagrams and engaging in self-quizzing using resources like the Holes Essentials textbook․
Leverage online companions and practice questions to reinforce concepts․ Focus on understanding relationships between structures and functions, and apply clinical examples for real-world context․
The study of anatomy and physiology provides foundational knowledge for healthcare and scientific advancements, as highlighted in Holes Essentials․
Future directions include integrating new technologies and research to enhance understanding of human systems and their functions․
10․1 Summary of Key Concepts
Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology provides a comprehensive understanding of the human body’s structure and functions․ It integrates anatomy and physiology, emphasizing how systems interact to maintain homeostasis․ Key concepts include the skeletal, muscular, nervous, and circulatory systems, as well as digestion, respiration, and reproduction․ The textbook is designed for learners with limited science backgrounds, offering clear explanations supported by visuals and clinical examples․ It prepares students for healthcare careers by linking theoretical knowledge to practical applications, ensuring a strong foundation for future studies and real-world scenarios․
10․2 Application of Anatomy and Physiology in Real Life
Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology bridges theoretical knowledge with practical applications, such as injury recovery, disease diagnosis, and physical therapy․ Understanding human systems aids in developing treatments and improving health outcomes․ For instance, knowing muscle functions can enhance physical training, while grasping circulatory processes can inform heart disease management․ This knowledge is vital for healthcare professionals, athletes, and individuals seeking to maintain overall well-being, making anatomy and physiology indispensable in daily life and professional settings․
10․3 Advances in the Field of Anatomy and Physiology
Recent advancements in imaging technologies and molecular research have deepened our understanding of human anatomy and physiology․ Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology incorporates these discoveries, offering insights into cellular mechanisms and system interactions․ Such progress aids in developing innovative treatments and improving diagnostic accuracy․ These advancements also enhance educational tools, making complex concepts more accessible for students and professionals alike, ensuring the field remains dynamic and relevant in modern healthcare and scientific exploration․