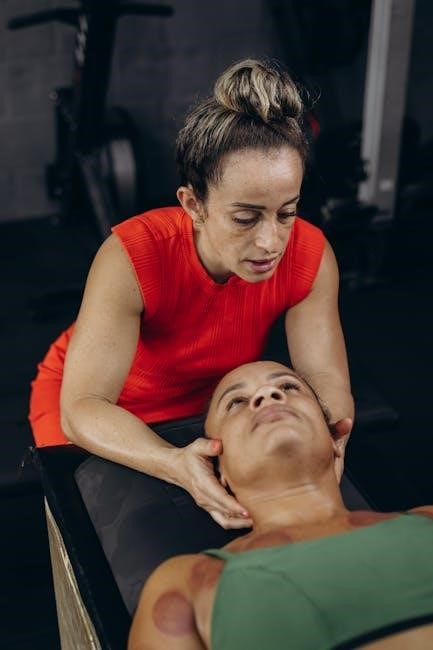
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) is a non-invasive assessment tool used in functional medicine to evaluate muscle strength, function, and underlying health imbalances. It provides insights into physical, emotional, and energetic factors affecting patient health, guiding personalized treatment plans and rehabilitation strategies.
1;1 Definition and Overview of Manual Muscle Testing (MMT)
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) is a non-invasive diagnostic tool used in functional medicine to assess muscle strength, function, and underlying health imbalances. It involves evaluating muscle groups against resistance to identify weakness or imbalance. Based on the Oxford Scale, MMT grades strength from 0 to 5, providing insights into physical, emotional, and energetic factors. Widely used by chiropractors, physical therapists, and functional medicine practitioners, MMT helps create personalized treatment plans and monitor progress in rehabilitation. It is also integral to applied kinesiology, linking muscle function to organ health and meridian systems.
1.2 Importance of MMT in Functional Medicine
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) is vital in functional medicine for identifying muscle imbalances, guiding treatment plans, and monitoring rehabilitation progress. It provides insights into physical, emotional, and energetic factors affecting health. MMT helps practitioners assess muscle strength, detect weaknesses, and address underlying issues, making it a cornerstone for holistic, patient-centered care and optimal functional outcomes.
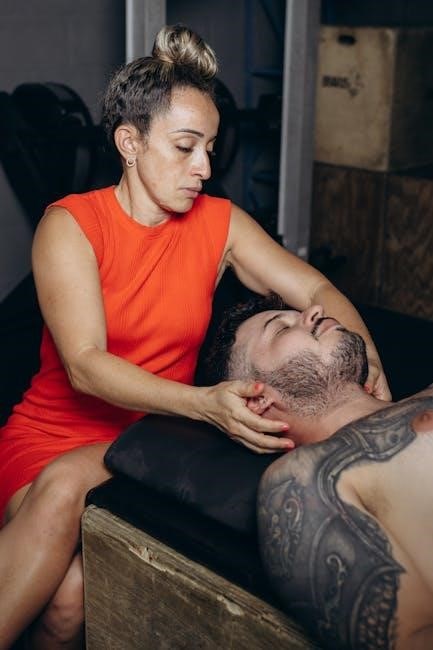

Key Principles of Manual Muscle Testing
Manual Muscle Testing is based on standardized techniques, including the Oxford Scale for strength grading, proper patient positioning, and the use of isometric break tests for accuracy.
2.1 Muscle Strength Grading Scales (Oxford Scale)
The Oxford Scale, also known as the Medical Research Council Manual Muscle Testing scale, grades muscle strength from 0 to 5. A grade of 0 indicates no movement, while 5 signifies full strength against resistance. This scale is widely used in functional medicine to assess muscle function objectively and consistently, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
2.2 Testing Techniques and Proper Patient Positioning
Proper patient positioning is crucial for accurate MMT results. Techniques involve testing specific muscle groups against resistance, ensuring full range of motion. Resistance is applied to assess strength, with grades based on the Oxford Scale. Correct positioning maximizes test reliability, ensuring consistent and reproducible outcomes in functional medicine assessments.
Applications of Manual Muscle Testing in Functional Medicine
Manual Muscle Testing is widely applied to assess muscle strength, identify imbalances, and guide treatment plans. It aids in evaluating functional movement patterns, monitoring rehabilitation progress, and optimizing patient outcomes in functional medicine.
3.1 Assessing Muscle Strength and Function
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) evaluates muscle strength and function by assessing key muscle groups against resistance. Using scales like the Oxford Scale, it grades strength from 0 to 5, providing a standardized method to identify weakness, monitor progress, and inform treatment strategies in functional medicine. This approach ensures precise and actionable insights for patient care.
3.2 Evaluating Functional Movement Patterns
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) helps assess functional movement patterns by evaluating how muscles work together during specific activities. It identifies imbalances, compensatory mechanisms, and limitations in coordination, providing insights into overall musculoskeletal function. This evaluation guides targeted interventions to restore optimal movement and improve functional outcomes in patients.
3.3 Identifying Muscle Imbalances and Weaknesses
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) is crucial for detecting muscle imbalances and weaknesses by evaluating strength and function. It identifies specific muscles or groups that are underactive or overactive, providing insights into biomechanical inefficiencies. This information helps practitioners design targeted interventions to restore balance, improve joint stability, and enhance overall musculoskeletal efficiency in functional medicine settings.
3.4 Monitoring Progress in Rehabilitation
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) is a valuable tool for tracking patient progress during rehabilitation. By regularly assessing muscle strength and function, practitioners can objectively measure improvements, adjust treatment plans, and ensure effective recovery. MMT provides clear, quantifiable data, helping to optimize rehabilitation outcomes and maintain patient motivation throughout the healing process in functional medicine.
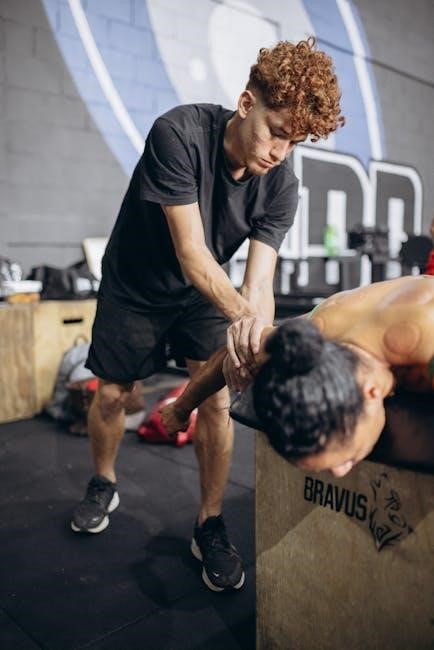

The Role of Applied Kinesiology in Functional Medicine
Applied Kinesiology (AK), developed by George Goodheart Jr. in 1964, is a diagnostic method in functional medicine using muscle testing to assess and address structural, muscular, and energetic imbalances.
4.1 Basics of Applied Kinesiology (AK)
Applied Kinesiology (AK) is a diagnostic technique that evaluates muscle strength to identify structural, chemical, and emotional imbalances. Developed by George Goodheart Jr., it combines manual muscle testing with holistic principles to assess the body’s response to various stimuli, aiding in pinpointing underlying health issues and guiding targeted therapeutic interventions. It emphasizes muscle function as a key indicator of overall well-being.
4.2 Using AK to Assess Nutritional and Energetic Balance
Applied Kinesiology (AK) employs muscle testing to evaluate nutritional deficiencies and energetic imbalances. By assessing muscle strength changes in response to specific stimuli, practitioners identify necessary nutrients or corrections. This method helps tailor dietary and supplement recommendations, restoring balance and optimizing bodily function, making it a valuable tool in functional medicine for holistic health management and preventive care.
Muscle-Organ-Meridian Connections
Muscles correspond to specific organs and meridians, with each muscle reflecting the health of its associated organ. Stimulation of related acupuncture points can improve organ function and overall well-being.
5.1 The Relationship Between Muscles and Organs
In functional medicine, muscles are linked to specific organs and meridians, with each muscle reflecting the health of its corresponding organ. Weakness in a muscle may indicate dysfunction in its associated organ, enabling practitioners to identify systemic imbalances. This connection is central to diagnostic and therapeutic approaches, such as stimulating acupuncture points to restore organ function and overall well-being.
5.2 Stimulation of Acupuncture Points for Organ Function
Acupuncture points corresponding to specific organs can be stimulated to address muscle-related imbalances identified through MMT. By targeting these points, practitioners aim to restore organ function, improve energy flow, and enhance overall health. This integrative approach combines manual muscle testing with traditional Chinese medicine principles to promote holistic healing and systemic balance in functional medicine practices.
Reliability and Validity of Manual Muscle Testing
MMT’s reliability and validity are enhanced through consistent techniques and the Oxford Scale, ensuring accurate muscle strength assessments in clinical practice and functional medicine applications.
6.1 Enhancing the Reliability of MMT
Consistency in testing techniques and proper patient positioning are critical to enhancing MMT reliability. Standardized grading scales, such as the Oxford Scale, ensure uniformity in assessments. Minimizing variability in testing conditions and ensuring examiner training further improve accuracy, making MMT a dependable tool for functional medicine practitioners to evaluate muscle function effectively.
6.2 Validity of MMT in Clinical Practice
MMT is widely accepted in clinical practice for assessing muscle strength and function. Its validity is supported by consistent use of standardized grading scales, such as the Oxford Scale, ensuring reproducible results. MMT provides actionable insights into muscle imbalances and functional limitations, making it a valuable diagnostic tool for guiding treatment plans in functional medicine settings.
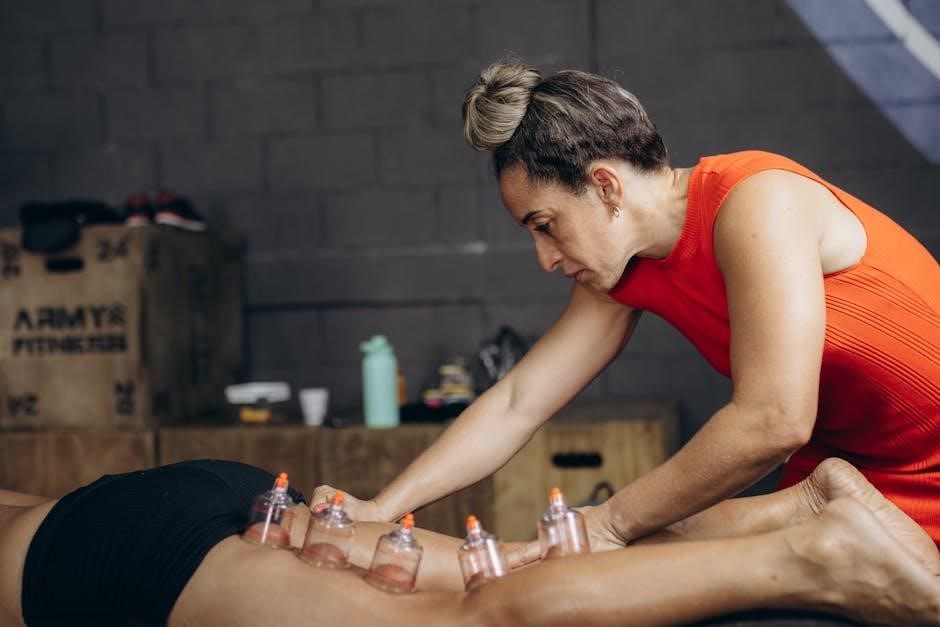

Practical Considerations and Diagnostic Techniques
Practical considerations include proper patient positioning, clear movement demonstration, and accurate resistance application. Diagnostic techniques like the Standing Functional Test and Isometric Break Tests provide valuable clinical insights.
7.1 Standing Functional Test (SFT) in SIJ Assessment
The Standing Functional Test (SFT) evaluates sacroiliac joint (SIJ) function by assessing pain provocation and movement patterns. Patients perform weight-bearing exercises, and the examiner observes for instability or discomfort, aiding in diagnosing SIJ dysfunction. This test complements manual muscle testing by providing dynamic insights into joint stability and functional movement quality.
7.2 The Use of Isometric Break Tests
Isometric Break Tests involve applying controlled resistance to assess muscle strength and endurance. This method evaluates the patient’s ability to sustain muscle contraction against external force, providing insights into functional capacity and imbalances. It is crucial for identifying weaknesses and monitoring progress in rehabilitation, ensuring targeted and effective treatment strategies in functional medicine.
Case Studies and Clinical Applications
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) plays a vital role in functional medicine through real-world applications, showcasing its effectiveness in rehabilitation and treatment success. Case studies highlight improved patient outcomes, demonstrating MMT’s impact on enhancing recovery and functional capabilities.
8.1 Real-World Examples of MMT in Functional Medicine
MMT has been effectively used in chiropractic care to address spinal misalignments and muscle imbalances. For instance, a patient with chronic low back pain showed significant improvement after targeted MMT-based interventions. Similarly, physical therapists use MMT to guide post-injury rehabilitation, ensuring optimal recovery. Such real-world applications highlight MMT’s practical role in enhancing functional medicine outcomes and patient well-being.
8.2 Success Stories in Rehabilitation and Treatment
A patient with chronic shoulder pain achieved full mobility after MMT-guided therapy. Another individual recovered from a sports injury using MMT to identify and strengthen weakened muscles. These success stories highlight how MMT-based interventions lead to personalized treatment plans, enhancing recovery and improving overall well-being in functional medicine practices.
Training and Certification in Manual Muscle Testing
Workshops and educational resources offer comprehensive training programs in MMT, providing hands-on experience and expert contributions for professionals seeking certification programs in functional medicine.
9.1 Educational Resources and Workshops
Educational resources and workshops provide comprehensive training in MMT, offering hands-on experience and expert contributions. These programs include instructional videos, manuals, and practical sessions, enabling professionals to master MMT techniques effectively for functional medicine applications.
9.2 Expert Contributions to the Field
Experts like Dr. Joseph Shafer have significantly advanced MMT through instructional videos and research, emphasizing its role in functional medicine. Their contributions provide deeper insights into neuromuscular diagnostics, enhancing clinical applications and educational standards for professionals worldwide.
Future Directions in Manual Muscle Testing
Future advancements in MMT may include integration with emerging technologies, such as AI and wearable devices, to enhance diagnostic precision and expand its applications in functional medicine.
10.1 Advances in Diagnostic Techniques
Emerging technologies like AI and wearable sensors promise to revolutionize MMT by enhancing accuracy and enabling real-time monitoring. These tools could provide deeper insights into muscle function, aiding in early detection of imbalances and personalized treatment plans, thus advancing the role of MMT in functional medicine.
10.2 Integration with Emerging Technologies
Manual Muscle Testing is increasingly being integrated with wearable devices and AI to enhance accuracy and real-time monitoring. These technologies enable precise data collection and analysis, supporting personalized treatment plans. The fusion of MMT with digital tools improves diagnostic capabilities, making it a more dynamic and efficient approach in functional medicine and rehabilitation.

Common Misconceptions About Manual Muscle Testing
Manual Muscle Testing is often misunderstood as pseudoscience, but it is a validated diagnostic tool in functional medicine. It assesses more than just muscle strength, providing insights into nutritional, emotional, and energetic imbalances, making it a holistic approach to patient care.
11.1 Addressing Skepticism and Criticisms
Despite its widespread use, Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) faces skepticism due to perceived subjectivity. Critics argue that results may vary based on examiner skill and patient effort. However, standardized techniques and proper training enhance reliability. MMT is a validated diagnostic tool in functional medicine, offering insights into muscle function, organ relationships, and systemic health, making it a valuable asset in clinical practice.
11.2 Clarifying the Scope of MMT in Functional Medicine
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) is a diagnostic tool with a focused scope in functional medicine, primarily assessing muscle strength, function, and imbalance. It aids in identifying nutritional deficiencies, energetic imbalances, and organ dysfunction through muscle-organ-meridian connections. MMT is not a standalone diagnostic but complements other assessments, offering a holistic view of patient health for targeted interventions and treatments.
Best Practices for Performing Manual Muscle Testing
Ensure proper patient positioning, clear communication, and consistent resistance application. Use standardized grading scales and document findings accurately for reliable and reproducible results in functional assessments.
12.1 Ensuring Patient Comfort and Safety
Patient comfort and safety are paramount in MMT. Ensure proper positioning to avoid strain or injury. Communicate clearly with the patient, explaining each step to reduce anxiety. Use gentle, controlled resistance and monitor for pain or discomfort. Adjust testing techniques for individuals with physical limitations to ensure a safe and effective assessment process.
12.2 Maintaining Consistency in Testing Protocols
Consistency in MMT protocols is crucial for accurate and reliable results. Use standardized testing methods, such as the Oxford Scale, to ensure uniformity across assessments. Proper training and adherence to established guidelines help maintain precision. Documenting results thoroughly and minimizing variability between examiners ensures reproducible outcomes, enhancing the validity and comparability of muscle testing in clinical practice.
Manual Muscle Testing is a cornerstone in functional medicine, offering insights into muscle function and holistic health. Its evolution underscores its integral role in modern diagnostic and therapeutic practices.
13.1 The Evolution of MMT in Modern Medicine
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) has evolved from a basic assessment tool to a sophisticated diagnostic method in modern medicine. Initially focused on muscle strength grading, MMT now integrates with advanced techniques like Applied Kinesiology, offering deeper insights into structural, nutritional, and energetic imbalances. This evolution highlights its adaptability and growing relevance in functional medicine, enhancing patient care and rehabilitation outcomes significantly.
13.2 The Integral Role of MMT in Functional Medicine
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) plays a vital role in functional medicine by aiding in the diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring of patient progress. Its non-invasive nature allows practitioners to assess muscle function, identify imbalances, and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. MMT’s holistic approach aligns with functional medicine’s focus on addressing the root causes of health issues, enhancing overall patient outcomes and care;